Imagine this:
Oliver: … Thus we see that donating to the opera is the best way of promoting the arts.
Eleanor: Okay, but I’m principally interested in improving human welfare.
Oliver: Oh! Well I think it is also the case that donating to the opera is best for improving human welfare too.
Generally, what is best for one thing is usually not the best for something else, and thus Oliver’s claim that donations to opera are best for the arts and human welfare is surprising. We may suspect bias: that Oliver’s claim that the Opera is best for the human welfare is primarily motivated by his enthusiasm for opera and desire to find reasons in favour, rather than a cooler, more objective search for what is really best for human welfare.
The rest of this essay tries to better establish what is going on (and going wrong) in cases like this. It is in three parts: the first looks at the ‘statistics’ of convergence - in what circumstances is it surprising to find one object judged best by the lights of two different considerations? The second looks more carefully at the claim of bias: how it might be substantiated, and how it should be taken into consideration. The third returns to the example given above, and discusses the prevalence of this sort of error ‘within’ EA, and what can be done to avoid it.
Varieties of convergence
Imagine two considerations, X and Y, and a field of objects to be considered. For each object, we can score it by how well it performs by the lights of the considerations of X and Y. We can then plot each object on a scatterplot, with each axis assigned to a particular consideration. How could this look?
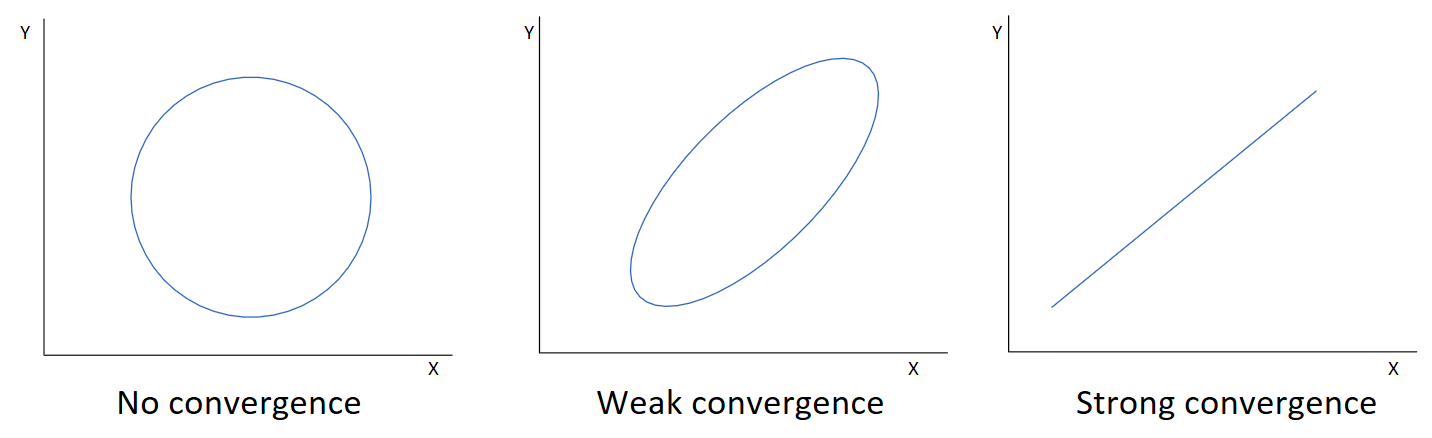
At one extreme, the two considerations are unrelated, and thus the scatterplot shows no association. Knowing how well an object fares by the lights of one consideration tells you nothing about how it fares by the lights of another, and the chance that the object that scores highest on consideration X also scores highest on consideration Y is very low. Call this no convergence.
At the other extreme, considerations are perfectly correlated, and the ‘scatter’ plot has no scatter, but rather a straight line. Knowing how well an object fares by consideration X tells you exactly how well it fares by consideration Y, and the object that scores highest on consideration X is certain to be scored highest on consideration Y. Call this strong convergence.
In most cases, the relationship between two considerations will lie between these extremes: call this weak convergence. One example is there being a general sense of physical fitness, thus how fast one can run and how far one can throw are somewhat correlated. Another would be intelligence: different mental abilities (pitch discrimination, working memory, vocabulary, etc. etc.) all correlate somewhat with one another.
More relevant to effective altruism, there also appears to be weak convergence between different moral theories and different cause areas. What is judged highly by (say) Kantianism tends to be judged highly by Utilitarianism: although there are well-discussed exceptions to this rule, both generally agree that (among many examples) assault, stealing, and lying are bad, whilst kindness, charity, and integrity are good.(1) In similarly broad strokes what is good for (say) global poverty is generally good for the far future, and the same applies for between any two ‘EA’ cause areas.(2)
In cases of weak convergence, points will form some some sort of elliptical scatter, and knowing how an object scores on X does tell you something about how well it scores on Y. If you know that something scores highest for X, your expectation of how it scores for Y should go upwards, and the chance of it also scores highest for Y should increase. However, the absolute likelihood of it being best for X and best for Y remains low, for two main reasons:

Trade-offs: Although consideration X and Y are generally positively correlated, there might be a negative correlation at the far tail, due to attempts to optimize for X or Y at disproportionate expense for Y or X. Although in the general population running and throwing will be positively correlated with one another, elite athletes may optimize their training for one or the other, and thus those who specialize in throwing and those who specialize in running diverge. In a similar way, we may think believe there is scope for similar optimization when it comes to charities or cause selection.

Chance: (c.f.) Even in cases where there are no trade-offs, as long as the two considerations are somewhat independent, random fluctuations will usually ensure the best by consideration X will not be best by consideration Y. That X and Y only weakly converge implies other factors matter for Y besides X. For the single object that is best for X, there will be many more not best for X (but still very good), and out of this large number of objects it is likely one will do very well on these other factors to end up the best for Y overall. Inspection of most pairs of correlated variables confirms this: Those with higher IQ scores tend to be wealthier, but the very smartest aren’t the very wealthiest (and vice versa), serving fast is good for tennis, but the very fastest servers are not the best players (and vice versa), and so on. Graphically speaking, most scatter plots bulge in an ellipse rather than sharpen to a point.
The following features make a single object scoring highest on two considerations more likely:
- The smaller the population of objects. Were the only two options available to OIiver and Eleanor, “Give to the Opera” and “Punch people in the face”, it is unsurprising the former comes top for many considerations.
- The strength of their convergence. The closer the correlation moves to collinearity, the less surprising finding out something is best for both. It is less surprising the best at running 100m is best at running 200m, but much more surprising if it transpired they threw discus best too.
- The ‘wideness’ of the distribution. The heavier the tails, the more likely a distribution is to be stretched out and ‘sharpen’ to a point, and the less likely bulges either side of the regression line are to be populated. (I owe this to Owen Cotton-Barratt)
In the majority of cases (including those relevant to EA), there is a large population of objects, weak convergence and (pace the often heavy-tailed distributions implicated) it is uncommon for one thing to be best b the lights of two weakly converging considerations.
Proxy measures and prediction
In the case that we have nothing to go on to judge what is good for Y save knowing what is good for X. Our best guess for what is best for Y is what is best for X. Thus the Opera is the best estimate for what is good for human welfare, given only the information that it is best for the arts. In this case, we should expect our best guess to be very likely wrong. Although it is more likely than any similarly narrow alternative (“donations to the opera, or donations to X-factor?”) Its absolute likelihood relative to the rest of the hypothesis space is very low (“donations to the opera, or something else?”).
Of course, we usually have more information available. Why not search directly for what is good for human welfare, instead of looking at what is good for the arts? Often searching for Y directly rather than a weakly converging proxy indicator will do better: if one wants to select a relay team, selecting based on running speed rather than throwing distance looks a better strategy. Thus finding out a particular intervention (say the Against Malaria Foundation) comes top when looking for what is good for human welfare provides much stronger evidence it is best for human welfare than finding out the opera comes top when looking for what is good for a weakly converging consideration.(3)
Pragmatic defeat and Poor Propagation
Eleanor may suspect bias is driving Oliver’s claim on behalf of the opera. The likelihood of the opera being best for both the arts and human welfare is low, even taking their weak convergence into account. The likelihood of bias and motivated cognition colouring Oliver’s judgement is higher, especially if Oliver has antecedent commitments to the opera. Three questions: 1) Does this affect how she should regard Oliver’s arguments? 2) Should she keep talking to Oliver, and, if she does, should she suggest to him he is biased? 3) Is there anything she can do to help ensure she doesn’t make a similar mistake?
Grant Eleanor is right that Oliver is biased. So what? It entails neither he is wrong nor the arguments he offers in support are unsound: he could be biased and right. It would be a case of the genetic fallacy (or perhaps ad hominem) to argue otherwise. Yet this isn’t the whole story: informal ‘fallacies’ are commonly valuable epistemic tools; we should not only attend to the content of arguments offered, but argumentative ‘meta-data’ such as qualities of the arguer as well.(4)
Consider this example. Suppose you are uncertain whether God exists. A friendly local Christian apologist offers the reasons why (in her view) the balance of reason clearly favours Theism over Atheism. You would be unwise to judge the arguments purely ‘on the merits’: for a variety of reasons, the Christian apologist is likely to have slanted the evidence she presents to favour Theism; the impression she will give of where the balance of reason lies will poorly track where the balance of reason actually lies. Even if you find her arguments persuasive, you should at least partly discount this by what you know of the speaker.
In some cases it may be reasonable to dismiss sources ‘out of hand’ due to their bias without engaging on the merits: we may expect the probative value of the reasons they offer, when greatly attenuated by the anticipated bias, to not be worth the risks of systematic error if we mistake the degree of bias (which is, of course, very hard to calculate); alternatively, it might just be a better triage of our limited epistemic resources to ignore partisans and try and find impartial sources to provide us a better view of the balance of reason.
So: should Eleanor stop talking to Oliver about this topic? Often, no. First (or maybe zeroth), there is the chance she is mistaken about Oliver being biased, and further discussion would allow her to find this out. Second, there may be tactical reasons: she may want to persuade third parties to their conversation. Third, she may guess further discussion is the best chance of persuading Oliver, despite the bias he labours under. Fourth, it may still benefit Eleanor: although bias may undermine the strength of reasons Oliver offers, they may still provide her with valuable information. Being too eager to wholly discount what people say based on assessments of bias (which are usually partly informed by object level determinations of various issues) risks entrenching one’s own beliefs.
Another related question is whether it is wise for Eleanor to accuse Oliver of bias. There are some difficulties. Things that may bias are plentiful, thus counter-accusations are easy to make: (“I think you’re biased in favour of the opera due to your prior involvement”/”Well, I think you’re biased against the opera due to your reductionistic and insufficiently holistic conception of the good.”) They are apt to devolve into the personally unpleasant (“You only care about climate change because you are sleeping with an ecologist”) or the passive-aggressive (“I’m getting really concerned that people who disagree with me are offering really bad arguments as a smokescreen for their obvious prejudices”). They can also prove difficult to make headway on. Oliver may assert his commitment was after his good-faith determination that opera really was best for human welfare and the arts. Many, perhaps most, claims like these are mistaken, but it can be hard to tell (or prove) which.(5)
Eleanor may want to keep an ‘internal look out’ to prevent her making a similar mistake to Oliver. One clue is a surprising lack of belief propagation: we change our mind about certain matters, and yet our beliefs about closely related matters remain surprisingly unaltered. In most cases where someone becomes newly convinced of (for example) effective altruism, we predict this should propagate forward and effect profound changes to their judgements on where to best give money or what is the best career for them to pursue. If Eleanor finds in her case that this does not happen, that in her case her becoming newly persuaded by the importance of the far future does not propagate forward to change her career or giving, manifesting instead in a proliferation of ancillary reasons that support her prior behaviour, she should be suspicious of this surprising convergence between what she thought was best then, and what is best now under considerably different lights.
EA examples
Few Effective altruists seriously defend the opera as a leading EA cause. Yet the general problem of endorsing surprising and suspicious convergence remains prevalent. Here are some provocative examples:
- The lack of path changes. Pace personal fit, friction, sunk capital, etc. it seems people who select careers on ‘non EA grounds’ often retain them after ‘becoming’ EA, and then provide reasons why (at least for them) persisting in their career is the best option.
- The claim that, even granting the overwhelming importance of the far future, it turns out that animal welfare charities are still the best to give to, given their robust benefits, positive flow through effects, and the speculativeness of far future causes.
- The claim that, even granting the overwhelming importance of the far future, it turns out that global poverty charities are still the best to give to, given their robust benefits, positive flow through effects, and the speculativeness of far future causes.
- Claims from enthusiasts of Cryonics or anti-aging research that this, additional to being good for their desires for an increased lifespan, is also a leading ‘EA’ buy.
- A claim on behalf of veganism that it is the best diet for animal welfare and for the environment and for individual health and for taste.
All share similar features: one has prior commitments to a particular cause area or action. One becomes aware of a new consideration which has considerable bearing on these priors. Yet these priors don’t change, and instead ancillary arguments emerge to fight a rearguard action on behalf of these prior commitments - that instead of adjusting these commitments in light of the new consideration, one aims to co-opt the consideration to the service of these prior commitments.
Naturally, that some rationalize doesn’t preclude others being reasonable, and the presence of suspicious patterns of belief doesn’t make them unwarranted. One may (for example) work in global poverty due to denying the case for the far future (via a person affecting view, among many other possibilities) or aver there are even stronger considerations in favour (perhaps an emphasis on moral uncertainty and peer disagreement and therefore counting the much stronger moral consensus around stopping tropical disease over (e.g.) doing research into AI risk as the decisive consideration).
Also, for weaker claims, convergence is much less surprising. Were one to say on behalf of veganism: “It is best for animal welfare, but also generally better for the environment and personal health than carnivorous diets. Granted, it does worse on taste, but it is clearly superior all things considered”, this seems much less suspect (and also much more true) than the claim it is best by all of these metrics. It would be surprising if the optimal diet for personal health did not include at least some animal products.
Caveats aside, though, these lines of argument are suspect, and further inspection deepens these suspicions. In sketch, one first points to some benefits the prior commitment has by the lights of the new consideration (e.g. promoting animal welfare promotes antispeciesism, which is likely to make the far future trajectory go better), and second remarks about how speculative searching directly on the new consideration is (e.g. it is very hard to work out what we can do now which will benefit the far future).(6)
That the argument tends to end here is suggestive of motivated stopping. For although the object level benefits of (say) global poverty are not speculative, their putative flow-through benefits on the far future are speculative. Yet work to show that this is nonetheless less speculative than efforts to ‘directly’ work on the far future is left undone.(7) Similarly, even if it is the case the best way to make the far future go better is to push on a proxy indicator, which one? Work on why (e.g.) animal welfare is the strongest proxy out of competitors also tends to be left undone.(8) As a further black mark, it is suspect that those maintaining global poverty is the best proxy almost exclusively have prior commitments to global poverty causes, mutatis mutandis animal welfare, and so on.
We at least have some grasp of what features of (e.g.) animal welfare interventions make them good for the far future. If this (putatively) was the main value of animal welfare interventions due to the overwhelming importance of the far future, it would seem wise to try and pick interventions which maximize these features. So we come to a recursion: within animal welfare interventions, ‘object level’ and ‘far future’ benefits would be expected to only weakly converge. Yet (surprisingly and suspiciously) the animal welfare interventions recommended by the lights of the far future are usually the same as those recommended on ‘object level’ grounds.
Conclusion
If Oliver were biased, he would be far from alone. Most of us are (like it or not) at least somewhat partisan, and our convictions are in part motivated by extra-epistemic reasons: be it vested interests, maintaining certain relationships, group affiliations, etc. In pursuit of these ends we defend our beliefs against all considerations brought to bear against them. Few beliefs are indefatigable by the lights of any reasonable opinion, and few policy prescriptions are panaceas. Yet all of ours are.
It is unsurprising the same problems emerge within effective altruism: a particular case of ‘pretending to actually try’ is ‘pretending to take actually arguments seriously’.(9)These problems seem prevalent across the entirety of EA: that I couldn’t come up with good examples for meta or far future cause areas is probably explained by either bias on my part or a selection effect: were these things less esoteric, they would err more often.(10)
There’s no easy ‘in house’ solution, but I repeat my recommendations to Eleanor: as a rule, maintaining dialogue, presuming good faith, engaging on the merits, and listening to others seems a better strategy, even if we think bias is endemic. It is also worth emphasizing the broad (albeit weak) convergence between cause areas is fertile common ground, and a promising area for moral trade. Although it is unlikely that the best thing by the lights of one cause area is the best thing by the lights of another, it is pretty likely it will be pretty good. Thus most activities by EAs in a particular field should carry broad approbation and support from those working in others.
I come before you a sinner too. I made exactly the same sorts of suspicious arguments myself on behalf of global poverty. I’m also fairly confident my decision to stay in medicine doesn’t really track the merits either – but I may well end up a beneficiary of moral luck. I’m loath to accuse particular individuals of making the mistakes I identify here. But, insofar as readers think this may apply to them, I urge them to think again.(11)
Notes
- We may wonder why this is the case: the content of the different moral theories are pretty alien to one another (compare universalizable imperatives, proper functioning, and pleasurable experiences). I suggest the mechanism is implicit selection by folk or ‘commonsense’ morality. Normative theories are evaluated at least in part by how well they accord to our common moral intuitions, and they lose plausibility commensurate to how much violence they do to them. Although cases where a particular normative theory apparently diverges from common sense morality are well discussed (consider Kantianism and the inquiring murder, or Utilitarianism and the backpacker), moral theories that routinely contravene our moral intuitions are non-starters, and thus those that survive to be seriously considered somewhat converge with common moral intuitions, and therefore one another.
- There may be some asymmetry: on the object level we may anticipate the ‘flow forward’ effects of global health on x-risk to be greater than the ‘flow back’ benefits of x-risk work on global poverty. However (I owe this to Carl Shulman) the object level benefits are probably much smaller than more symmetrical ‘second order’ benefits, like shared infrastructure, communication and cross-pollination, shared expertise on common issues (e.g. tax and giving, career advice).
- But not always. Some things are so hard to estimate directly, and using proxy measures can do better. The key question is whether the correlation between our outcome estimates and the true values is greater than that between outcome and (estimates of) proxy measure outcome. If so, one should use direct estimation; if not, then the proxy measure. There may also be opportunities to use both sources of information in a combined model.
- One example I owe to Stefan Schubert: we generally take the fact someone says something as evidence it is true. Pointing out relevant ‘ad hominem’ facts (like bias) may defeat this presumption.
- Population data – epistemic epidemiology, if you will – may help. If we find that people who were previously committed to the operas much more commonly end up claiming the opera is best for human welfare than than other groups, this is suggestive of bias.
A subsequent problem is how to disentangle bias from expertise or privileged access. Oliver could suggest that those involved in the opera gain ‘insider knowledge’, and their epistemically superior position explains why they disproportionately claim the opera is best for human welfare.
Some features can help distinguish between bias and privileged access, between insider knowledge and insider beliefs. We might be able to look at related areas, and see if ‘insiders’ have superior performance which an insider knowledge account may predict (if insiders correctly anticipate movements in consensus, this is suggestive they have an edge). Another possibility is to look at migration of beliefs. If there is ‘cognitive tropism’, where better cognizers tend to move from the opera to AMF, this is evidence against donating to the opera in general and the claim of privileged access among opera-supporters in particular. Another is to look at ordering: if the population of those ‘exposed’ to the opera first and then considerations around human welfare are more likely to make Oliver’s claims than those exposed in reverse order, this is suggestive of bias on one side or the other.
- Although I restrict myself to ‘meta’-level concerns, I can’t help but suggest the ‘object level’ case for these things looks about as shaky as Oliver’s object level claims on behalf of the opera. In the same way we could question: “I grant that the arts is the an important aspect of human welfare, but is it the most important (compared to, say, avoiding preventable death and disability)?” or “What makes you so confident donations to the opera are the best for the arts - why not literature? or perhaps some less exoteric music?” We can post similarly tricky questions to proponents of 2-4: “I grant that (e.g.) antispeciesism is an important aspect of making the far future go well, but is it the most important aspect (compared to, say, extinction risks)?” or “What makes you so confident (e.g) cryonics is the best way of ensuring greater care for the future - what about militating for that directly? Or maybe philosophical research into whether this is the correct view in the first place?”
It may well be that there are convincing answers to the object level questions, but I have struggled to find them. And, in honesty, I find the lack of public facing arguments in itself cause for suspicion.
- At least, undone insofar as I have seen. I welcome correction in the comments.
- The only work I could find taking this sort of approach is this.
- There is a tension between ‘taking arguments seriously’ and ‘deferring to common sense’. Effective altruism only weakly converges with common sense morality, and thus we should expect their recommendations to diverge. On the other hand, that something lies far from common sense morality is a pro tanto reason to reject it. This is better acknowledged openly: “I think the best action by the lights of EA is to research wild animal suffering, but all things considered I will do something else, as how outlandish this is by common sense morality is a strong reason against it”. (There are, of course, also tactical reasons that may speak against saying or doing very strange things.)
- This ‘esoteric selection effect’ may also undermine social epistemological arguments between cause areas:
It seems to me that more people move from global poverty to far future causes than people move in the opposite direction (I suspect, but am less sure, the same applies between animal welfare and the far future). It also seems to me that (with many exceptions) far future EAs are generally better informed and cleverer than global poverty EAs.
I don’t have great confidence in this assessment, but suppose I am right. This could be adduced as evidence in favour of far future causes: if the balance of reason favoured the far future over global poverty, this would explain the unbalanced migration and ‘cognitive tropism’ between the cause areas.
But another plausible account explains this by selection. Global poverty causes are much more widely known that far future causes. Thus people who are ‘susceptible’ to be persuaded by far future causes were often previously persuaded by global poverty causes, whilst the reverse is not true - those susceptible to global poverty causes are unlikely to encounter far future causes first. Further, as far future causes are more esoteric, they will be disproportionately available to better-informed people. Thus, even if the balance of reason was against the far future, we would still see these trends and patterns of believers.
I am generally a fan of equal-weight views, and of being deferential to group or expert opinion. However, selection effects like these make deriving the balance of reason from the pattern of belief deeply perplexing.
- Thanks to Stefan Schubert, Carl Shulman, Amanda MacAskill, Owen Cotton-Barratt and Pablo Stafforini for extensive feedback and advice. Their kind assistance should not be construed as either endorsement endorsement of the content, nor responsibility for any errors.

Excellent and underrated post. I actually told Greg a few years ago that this has become part of my cognitive toolkit and that I use this often (I think there are similarities to the Tinbergen Rule - a basic principle of effective policy, which states that to achieve n independent policy targets you need at at least n independent policy instruments).
This tool actually caused me to deprioritize crowdfunding with Let's Fund, which I realized was doing a multiobjective optimization problem (moving money to effective causes and doing research), and that I needed to focus on one thing.
Another instance in which I used this is in my climate policy paper, where I mentioned suspicious convergence:
"Advanced economies sometimes give aid to emerging economies for environmentally harmful projects: to increase tourism,[278] to build gas power plants,[279] and sometimes even to build coal power plants.[280] Does this reflect a lack of policy coherence? Why not fund projects that make sense from both the perspective of the climate and poverty reduction? For instance, one natural experiment in Brazil showed that paying “extremely poor households for forest conservation” reduced deforestation by 3-5%.[281] A recent randomized controlled trial[282] found that conditional cash transfers to forest-owning Ugandan farmers to conserve forest owned by them prevented emissions at a rate of $0.46 per ton of CO₂.[283]
Given that the lower bound for the social cost of carbon has been estimated to be $125 per ton,[284],[285] should there be a scaling up of such interventions? Would this policy-coherent approach to preventing both poverty and climate change be the most effective? We argue that—perhaps counterintuitively—it might not be.
At a first approximation, a policy-coherent approach appears preferable, and giving aid for gas plants seems counterproductive. However, gas will make up a non-trivial fraction of energy for the foreseeable future, and, in terms of emissions and air pollution it produces, gas is much better than coal. Energy access is vital for industrial development, which reduces poverty; despite the fact that it violates principles of policy coherence, it might be optimal to give aid for gas power. To get a bit more technical: Multi-objective optimization is generally harder than single-objective optimization.[286] It might therefore be more effective to optimize for poverty reduction or economic growth in aid project A, be that through fostering tourism or cheaper electricity access through gas. Then , in ‘aid’ project B (which then is not really an aid project, but a climate change project), one should optimize for the most effective climate change prevention . There is an allure to policy coherence and optimizing for several objectives at once, but it would be a suspicious convergence if the best poverty reduction methods happened to be the most effective ways to combat climate change as well.
Aid should reduce poverty and/or stimulate growth at the same time that other funding is used to combat climate change in the most effective way. One of these ways is performance-based pay for the conservation of rainforests.[287] For example, Norway pledged up to $1 billion in performance-based pay for the conservation of Brazilian rainforests. Preventing deforestation in Brazil is very cost-effective, at $13 per ton of CO₂ equivalent averted on average.[288] Performance targets can be independently verified through satellite imaging. Such efforts should be disconnected from aid budgets, while the international community could pay for the preservation of rainforests globally."
I think about this post all the time
I think of this post often - the pattern comes up in so many areas.
Thanks Greg, really interesting post. One thing to bear in mind I think is that people who are expected to have a prior commitment to a particular cause are often the ones called on to defend the view that all things considered that cause is most effective. For example, my view is that it is really difficult to know what cause is most effective, and I'm therefore deeply uncertain about it. But, as the person running Giving What We Can, it's often assumed that I think eradicating extreme poverty is the most effective cause area, and am therefore called on to defend that as a thesis. That means it's much more frequently the case that I'm steel-manning the view that eradicating extreme poverty is the best way to improve the far future than that stopping factory farming is. It seems somewhat useful to have this kind of specialisation, but it also means that it's easy for the people always steel manning one view to end up taking that on board more than other views, as well as for those around them to assume their rationalising when in fact they're deliberately steel-manning.
Michelle, I'm a little unclear about what you mean here. It didn't seem like the post was arguing against thinking that, all things considered, a given cause is most important. Rather, that the most important cause will still involve tradeoffs; it won't do everything best, and may be harmful in some ways. I don't see how that contradicts the need to defend global poverty as the most effective cause area, all things considered.
Also, I'm curious about who you steelman global poverty as the best far future cause against. For new/potential GWWC-ers, can't you just demonstrate why it's plausibly better than most things (I'm assuming these people aren't already into animal suffering alleviation or x-risk reduction. And if they are, why are you arguing with them?)? Or, better yet, say the issue is complicated and present the main important arguments?
Sorry it was rather unclear. I wasn't thinking of my post as disagreeing with Greg. I was trying to make two points: 1) Sometimes, when it seems like someone is saying 'eradicating existing extreme poverty is the best way to improve the far future' (which you might think seems plausibly caused by bias because you wouldn't expect the two to be strongly correlated), they might actually be saying 'here is the argument for why eradicating existing extreme poverty might be the best way to improve the far future'. 2) One of the causal mechanisms by which people come to believe the strong causal correlation in cases where that doesn't seem plausible is that by virtue of working in a particular cause area, they are often called on to defend that cause area as being also the best way of doing other things.
The kinds of cases I was thinking of: for EA Global I was asked to be on a panel as the person defending poverty as the most important cause area (where there were other panellists defending animal suffering and x-risk). The idea is that you get the best arguments coming out if you get one person to steel man each position, and then have a discussion amongst panellists, and the people most likely to be able to present a good case for a cause are those who spend their whole day thinking about that cause. I actually dislike this format, both because it encourages people to get entrenched in their own positions, and because it encourages people to see things as a combat amongst causes. (In the end I think EA Global Ox did a good job of getting people to steel man different views, and of concentrating on the debates rather than pitches - I actually ended up steelmanning movement building on that panel, and giving a separate talk steelmanning the case against movement building. But this is the kind of example I was thinking of where people are expected to defend the cause area they work in.) As you say, to new / potential GWWCers this doesn't come up.
I also wonder whether the 'equal and oppositely partisan' approach is a good way of getting to the fact of the matter. Apart from the detriments you mention, Michelle, it simply may not be a good way of getting to the best reasons than having panellests trying to be impartial.
(I also wonder whether steelmanning, although much better than the strawmanning, might be inferior to 'realmanning').
There is a subsection of animal advocates in effective altruism who are concerned that a far future in which anti-speciesism isn't prevalent isn't a worthy future. If that's a confusing wording, let Brian Tomasik, a thought leader in such circles, to explain. From "Risks From Astronomical Future Suffering" [emphasis mine]:
Thus, whatever charity can most effectively spread anti-speciesism, or other value-systems for reducing suffering, would be considered the most effective charity overall. If the most effective way to spread the anti-speciesist meme is an ACE-recommended charity spreading an animal-free diet, it is, by some lights, legitimately the most effective charity for far-future considerations. Again, to clarify, this wouldn't be perceived as a rationalization of convergence on specious grounds. It follows from a simple chain of reasoning that getting as many of the humans as possible who will steer the far future to care about non-human suffering, so they'll be inclined to prevent it rather than let it happen.
I just wanted to clarify there are some animal advocates in this community who believe promoting animal welfare is the best for the far future, not because it ensures human survival, but because it prevents the worst outcomes of human survival. This is different from the example provided above. One might consider this a niche position in effective altruism. On the other hand, multiple organizations out of Basel, Switzerland, supported by the Effective Altruism Foundation, are heavily influenced by the work of Brian Tomasik and allied colleagues. I don't know good data on how prevalent these concerns are, across all of effective altruism, or specifically among those who prioritize animal welfare/anti-specieism.
Your point is very much related to the argument that reducing anti-speciesism decreases s-risk.
Add this to the list?
‘Building massive mega- language models is a good way of increasing AI capabilities and it’s also the best thing for AI alignment and safety’
I think that the point about veganism doesn't follow from the rest of your piece, and could well be true depending on the object-level details. In the case of weak convergence, no point will maximise both X and Y, but a set of points may well contain the maxima of both X and Y - in fact, if the set of points consists of the upper-right end of the 'ellipse', it could be that no other point does much better than anything in the set on X or Y. Therefore, even if the best intervention for X isn't the best intervention for Y, it will be the case that the set of great interventions for X is almost the same as the set of great interventions for Y if X and Y are weakly correlated. Tying this back to veganism, it could well be that the set of vegan diets contain the best diet for animal suffering, the best diet for environmental impact, the best diet for tastiness, etc, and that vegan diets are better than all other diets on these metrics. Although on the object-level it seems unlikely that minimising animal suffering is correlated with tastiness in diets, it seems plausible enough that it is correlated with environmental impact.
Thanks for this. I agree it doesn't neatly follow from the principles earlier in the piece: if you measure diets monolithically, there are only a few, then it is not that surprising to have one keep coming top. Conversely, if measured as classes, as you say it becomes less surprising to find a particular (large) set of diets keep coming top.
However, I still think it is a bit surprising. I think on most reasonable measures vegan diets are a minority of the space of diets available - both in practice and in theory there are a lot more ways of having animal products and non-animal products than just the latter. So if this minority set keeps coming up top when looking at many disparate considerations, we should ask why. If it were just two, maybe that isn't so bad, but X, Y, Z, W etc. becomes more and more surprising.
(I agree with your determinations on the object level issues. There's a clear case for veganism being best for animal welfare, and that expectedly correlates with environmental impact, but less so health and taste. I wouldn't be altogether surprised to find that a diet optimized purely for low environmental impact might include some animal products, much less surprised if one for optimized for health did, and pretty confident one for taste would.)
Just an anecdote and bordering on off-topic I guess, but the "vegetarian/vegan tastes better/best than meat" is a point that I (a non-vegan!) have found myself defending multiple times. In fact, my safest bet when trying a new cuisine is to go for vegan-est dishes, for taste alone.
When I express this socially, I typically find others agreeing.
So this sprinkled insistence on "veganism defended for taste is suspicious" is suspicious to me, and makes me go meta. It's not the point of the post however so I'll drop it here.
My apologies, but could anyone help me find a half-remembered blog post about veganism which directly addresses this very intuitive objection?
The thesis that stayed with me is that veganism is not "too good to be true" because most of its features are not convergent, but correlated consequences of a single fact: animals are themselves evolved to optimize a goal which is not "being eaten" (in fact, it's almost exactly "not being eaten"!), and they are therefore suboptimal food-generating technologies. Specifically, animals put much of the energy they consume into action and cognition, instead of growing edible flesh; due to this inefficiency, they cause more emissions and require more freshwater and land than plant food; and they suffer when used as food machines, because they evolved to avoid predation. Consequently, we should not be surprised that we can develop technologies for converting plants into food that outperform animals across these metrics. (Notably, health and taste do not clearly follow from the same fact, and veganism is plausibly merely adequate rather than optimal on these metrics.)
Does anyone recognize the post I'm trying to paraphrase? I can't find it on Google, or in the pingbacks here.
This reminds me of Bryan Caplan: http://econlog.econlib.org/archives/2016/01/the_invisible_t.html
To continue the riff, we might say that the appropriate emotion for someone arguing that funding opera in fact maximises human welfare is surprise. "Now, I know you wouldn't expect this, but amazingly it turns out that..."
Your interlocutor might believe that funding opera maximises human welfare for good reasons. But if they don't seem to think that it's a remarkable fact, that suggests the opposite.
I have a hypothesis for why people are motivated to rationalise: It is very uncommon in EA to justify claims by taking their intrinsic values into account. It is assumed that EAs are "rational enough" to update their beliefs/change their career whenever they encounter arguments that are stronger than the previous ones. If pressed to explain themselves, the pattern described above often happens.
As an alternative response, it could be beneficial to create the norm that it is valid to care more about some causes than others. Most people have intrinsic values that are not always morally justifiable.
This approach would create more intellectual honesty and stop disguising the true motives for why people are motivated to work on specific causes.
I can also see the downside if taken to an extreme, for example, the inability to update one's beliefs since "Making Operas available to everyone is an intrinsic value of mine, so any critique on my chosen cause is futile".
Very good post. A common problem with ad hominem-arguments is that people often don't give any detailed reasons for believing that their opponent is biased, or for the connection between them being biased and them being wrong. Instead, they just vaguely point to a possible non-rational reason for why their opponents might be biased and wrong. (Cf "just-so-stories" in evolutionary psychology.) Here we get a much more detailed analysis of why this convergence is suspicious.
David Friedman addressing an instance of this issue:
http://www.daviddfriedman.com/Academic/Property/Property.html
In his dissertation near the end Josh Greene argues that in everyday cases utilitarianism's conflict with other moral accounts (like deontology) is less than one might have guessed because large harms or forgone benefits elicit moral campaigning that change moral intuitions (e.g. Mothers Against Drunk Driving making drunk driving seem intuitively bad even when no one is harmed in a particular case).
The opposite seems to happen as well - namely denying that something really is a harm because it is caused by a just policy, or happens to an unpopular group.
What is remarkable about this, of course, is the recognition of the need to address it.
What such a great post, thanks!